A very interesting topic of discussion. We have mail integrated to every application now a days. We integrate email using SMTP settings in the Web.Config in .NET and use the Send method to send mails. Recently, I came across an interesting challenge, where we were to send emails from our SQL Server. Suppose we have to track the successful scheduled sql query execution. We cannot look into the tables it modified every time in order to check if it actually ran through successfully. It would be so nice, if we could get some kind of notification which can help us know about the status of execution. Yes, it is possible to send mails from our sql server using few stored procedures which are actually pre-defined.
Lets learn how:-
Get Started
Remember we will be using pre defined Stored procedure to send the mails. First of all we need to set up an account with the credentials required by the server to send the mails. Usually the mail is sent through SMTP, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. The settings would depend on the server your aplication demands. Remember the configuration needs to be valid.
Create a Database Account:-
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_account_sp
@account_name = 'SendEmailSqlDemoAccount'
, @description = 'Sending SMTP mails to users'
, @email_address = '[email protected]'
, @display_name = 'Suraj Sahoo'
, @replyto_address = '[email protected]'
, @mailserver_name = 'smtp.gmail.com'
, @port = 587
, @username = 'XXXXXX'
, @password = 'XXXXXX'
GoPlease use proper credentials and server settings in order to successfully deliver the mails, else they will fail and be queued.
Nextstep is to create a profile which would be used to tconfigure the database mail. The sp would look like below:
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profile_sp
@profile_name = 'SendEmailSqlDemoProfile'
, @description = 'Mail Profile description'
GoThis profile would be used in order to set the mail configuration and the emails and sent.
Next step is to map the account to the profile. This will let the profile know, which account credentials it need to work for sending successfully.
That would look like:
-- Add the account to the profile
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profileaccount_sp
@profile_name = 'SendEmailSqlDemo'
, @account_name = 'SendEmailSql'
, @sequence_number = 1
GOThus, we are all set to send the successly emails. The mail sending look up snippet would look like below:
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'SendEmailSqlDemo2'
, @recipients = '[email protected]'
, @subject = 'Automated Test Results (Successful)'
, @body = 'The stored procedure finished successfully.'
, @importance ='HIGH'
GOThe stored procedured being used are sometimes vulnerable to not getting executed. So Try catch block and Begin and End Transaction are mandatory in few Stored Procedures.
Lets take an example here,
Suppose we have a SELECT INSERT query using Stored Procedure, so what happens is we are selecting and inserting from 4 tables, lets say
Users | UserLogin | UserEmployment | Departments
For each new screen creation we are manipulating and selecting the users based on their PK and inserting again into the same tables with a different FK, representing the particular screen. The query would look like below:-
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN TRAN
INSERT INTO
dbo.[User]
SELECT
us.UserName,
us.UserAddress,
us.UserPhone,
@fkScreenID
FROM
dbo.[User] as us
WHERE
UserID= @userID
COMMIT TRAN
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
ROLLBACK TRAN
END
END CATCH //Similarly for other tables as well we continue. Its is better to add the Try Catch to whole SP Executing BlockHere, when the transaction in case fails, it would move into the Catch block and there we can have the email sending procedure so as to get a notification regarding the success or failure and reason and where it failed. This would be so helpful for any developer.
Troubleshooting Mails
There are also stored procedure to let us know if the mails are successful, failed or remained in the queue. This is fascinating feature. :).
To check for the mails which were successfully sent and delivered, we run the below query:
select * from msdb.dbo.sysmail_sentitems
Some of the columns it returns are

![]()
In the second image you can see we have the sent_status as sent, which states the mail has been successfully sent.
To check for the unsent mails which could not be sent, we run the below query:
select * from msdb.dbo.sysmail_unsentitems
TO check for the failed mails, which will not even be retried to be sent from the queue, we run the below query:-
select * from msdb.dbo.sysmail_faileditems
For more details on the failure along with the reason, the trouble shoot query would look like:
SELECT items.subject,
items.last_mod_date
,l.description FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_faileditems as items
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.sysmail_event_log AS l
ON items.mailitem_id = l.mailitem_id
GO
The error description above is like “No Such Host” Error. This error usually comes when we have some smtp server connection settings wrong. We need to troubleshoot that on our own and recheck the settings credentials and then try. If then it does not seem to work, we need to look for the DNS server settings and retry with the configuration again. Nothing to worry for this though..:)
Conclusion
Thus we discussed here about sending mails from our own SQL using the stored procedures and how helpful they can prove to be. Troubleshooting the errors is very easy here and the set as well.
Exceptions and errors are a part of development which cannot be avoided but handling them is a challenge and developers can easily do that. 
CodeProject
References
]]>- SQL Basics
- Introduction
- What is a database?
- What does Relational mean?
- A small example
- SQL Statement
- Naming Things
- Creating Things
- Everything about SELECT Statement
- Introduction
- FROM Clause
- Limiting Result Set
- WHERE Clause
- WHERE Clause
- AND OR
- MORE Operators
- BETWEEN
- LIKE
- IN
- IS and ISNOT
SQL Basics
Introduction
Before I begin, this article is intended to each and every beginner may it be a Software Developer or a Quality Analyst, this is a must know for every software engineer. Some might say we have Database administrator, then why should we, but I feel being developer one should know all round knowledge of whats going on and handle everything.
Here in this article I will be explaining each and every concept in details to get started with SQL (Structured Query Language).
First of all, the question ![]() going on your mind now would be what is SQL?
going on your mind now would be what is SQL?
As mentioned above, SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It is a special-purpose programming language. Its purpose is to manipulate relational databases. Relational databases are one which have detailed information about all the tables in a formally organized manner. The best part here is it contains both the data-definition syntax as well as data-manipulation syntax.
What is a Database?
Now the diagram describes what it is.  Database is simple a container that helps organize data in a format or constructive manner. In a database data is stored in a rational way. Now, lets take an example that would make help understand better. For instance our contact list in cell phones. If we think a bit into it, then we realize the contact list is a database with data in it in an organized manner. Then we sort by the letters search the names from the list. Thus we perform query execution on the list to retrieve the records we want. This is the flexibility a simple database provides us. It makes it easier to:
Database is simple a container that helps organize data in a format or constructive manner. In a database data is stored in a rational way. Now, lets take an example that would make help understand better. For instance our contact list in cell phones. If we think a bit into it, then we realize the contact list is a database with data in it in an organized manner. Then we sort by the letters search the names from the list. Thus we perform query execution on the list to retrieve the records we want. This is the flexibility a simple database provides us. It makes it easier to:
- Query Data
- Update Data
- Insert New Data
- Delete Data
There are basically three types of Databases available:
- Relational Database
- Object-Oriented:-Link to refer
- Document Based:-Link to refer
We will be discussing only on the Relational Database as that is commonly used. I have provided the links to the other types of databases for reference.
What is Relational?
The dictionary meaning to this is “Things that relate each other in a way”. Here the meaning does keeps it consistency. Relational model is the database model on which SQL is based. It is thus a way to describe data and the relationship between those data entities.
In a relational database, data is stored in a construct called Table. Now what is a Table?
- A table is a collection of columns that define the table properties with specific datatype associated, with specific size, thus restricting the size of each record to be inserted into the table.
- Every column can be made required or not required(using the check box available for Null values).
- Rows can be retrieved by asking questions about the data. Like “You would need all the rows of data that have a column(surname) value as having value ‘Ray'”
- An essential part of a table is “Key”. Every table must have a key associated with any column to uniquely identify a table. Usually a table is associated with a key called Primary Key.(We will be discussing about keys in the upcomin modules).
- If more than one table uses the same primary key (one table-Primary key and other named foreign key), then the tables can be merged or joined to give different set of records set.
A small Example
Before starting with the, I hope the readers have a view of the SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio). Here is how the SSMS looks like:
Now lets ask questions to ourself. Why do we at all need database with multiple tables, why not a single table! lets check with an example why?
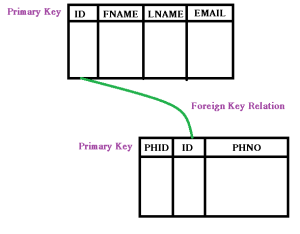
Suppose we have a User table which would have columns named UserID, FName, LName, Email & PhNo. Now suppose we have only this table and there is a requirement in the future that a user may have more than one Phone number or more than one Email. Just think how would we approch to this, as we cannot store multiple values into a column. Thus, does not this give us an indication to have another table! Just see the difference below:-
In the above figures, you can see the difference clearly, using the first table will cause real problem and a lot of redundant data/records in the table which anyway violates the Normalization rules (Normalization Rules). Thus creating the secod table which would be having a foreign key relationship with the User table, can now store as many phone numbers as a user can have.
SQL Statement
- A SQL statement is framed from the combination of actionable set of vali words out of which some are SSMS defined and others are user defined.
- A valid SQL statement would be if a statement/query ends with a semicolon (;), it is not like that its mandatory to add semicolon at the end. But it is a part of the ANSI standard, so itisadvisable to use the semicolon at the end of the statement.
- SQL is not case-sensitive. Usually the queries/statements are written in Caps(Capitals). Sometimes the user-defined functions are in the lower case. But oviously the standard needs to be followed for better maintenance and maintain consistency.
- In SQL statement, we can put comments. For single line comments, “–” is used as predecessor for the query as single line comment where as “/**/”, is used for the query as multiple line comments.
- SQL statements start with commands. Comparing with the english language, the commands here are similar to the verbs. For example, SELECT(Command/keyword in SQL)
In generic terms, SELECT would go like below:SELECT VALUES FROM TABLE NAME;
After the command comes the part that is highly dependent on the commands that is to define the set of result/records we would expect from the query like a list of all values of the columns (genrally the wildcard symbol “*” asterix is used to select all columns in table). Then is the FROM clause which is used to fetch records/ column values from which table(as it explains itself).
Naming Things
This might be a bit controversial, as there is nothing called best way to do. So we follow what is followed the most, or follow the conventions already been used. This would differ from person to person. But the most important factor to keep in mind is to have consistency through out. So, that when we see the database the names of the tables define themselves. Some of the rules I am listing below:
- Table name should be singular. A table name describes what the values would be in a row. It is not a hard bound rule, but a rule.

- Column names in a table should not repeat themselves and also same applies at the database level. The repeatation is only allowed when there is a relationship between tables.
- Names are “scoped” in SQL. What this means is a database would have a name. Tables inside database should have a name. Thus while accessing the table, it should be accessed with its “full” name wj=hich would include the database name, separated by periods.
Like TableName:- DatabaseName.Table
ColumnName:- Table.Column
Creating Things
There is a whole set of SQL commands which are required to create and modify the structures/records in the database.
CREATE DATABASE DemoDatabase;
USE DemoDatabase;
CREATE Table DemoDatabase.DemoTable(…);
Here I have only shown the structures, we will be discussing more that ahead.
Datatypes are very vital when we will be creating the tables in a database. Each column in a database has restriction on the datatype of the data that can be stored in the table.
Lets have a look at the datatypes:-
| Data Type | Value/Space |
|---|---|
| CHARACTER | Can hold ‘N’ number of characters which are specified implicitly, to be exact statically that is the number of characters to be accepted in the vallue is set at the time of column creation |
| VARYING CHARACTER | Can hold ‘N’ characters which is set dynamically, that is if MAX is set then it would accept any number of characters sent from the server into the column. |
| BINARY | Stores Hexadecimal data, fixed length with a length of n bytes, where n varies from 1 through 8,000. Used for images and other sort of blobs. |
| VAR BINARY | As the name suggests, it accepts value of varying length. When size is not specified, then default value is taken as 1. |
| SMALLINT | Its length is 2 bytes and ranges from -2^15 (-32,768) to 2^15-1 (32,767) |
| INT | Its length is 4 bytes and ranges from -2^31 (-2,147,483,648) to 2^31-1 (2,147,483,647) |
| BIGINT | Its length is 8 bytes and ranges from -2^63 (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808) to 2^63-1 (9,223,372,036,854,775,807) |
| TINYINT | Its length is 1 byte and ranges from 0-255. Can be used for values with Yes/No or the enumeration types which are limited to fewer values |
| BOOLEAN | Stores TRUE FALSE values. When NOT NULLABLE, then default value is False, else it also accept NULL values. |
| DATE | Stores only Date values, only YEAR MONTH & DAY values in the format YYYY–MM–DD |
| TIME | Stores only time values, only HOUR MINUTE & SECONDS values of a day in the format HH–MM–SS |
| TIMESTAMP | Stores both date & time. This is when date is combined with time of a day with the seconds. Format is just concating both date format and time format |
These are some of the datatypes, I have listed out. The important thing here to keep in mind is, while creating the table, we never actually keep in mind. Thus the datatype play a very important role if we consider the future. Suppose we use the number of user or the userid in a table datatype as smallint or only int even, then sometimes in future may be the number of users increases to a large extent and overlaps the range of the datatypes. Then here the problem arises. You might have heard about the youtube crash for the Gangnam song. The reason behind it was this the issue with the datatype for the number of views..It increased to such extent that it crashed.
Relational Database Management System is based on the relational model. In simple terms, it is a type of database management which stores data in realated tables.
Everything about SELECT statement
Introduction
As we have already discussed about the SSMS where we will be demonstrating our queries. After you read through this part of the article, you would be able to understand the details of using the SELECT statement, asking different types of questions to the select query.
First of all, we store the data in a database to reuse it at some later point of time. Querying data is all about asking questions while retrieving data. Understanding the combination of english and the SQL helps us postulate the queries very easily.
Lets create a database first. Look below at the query.
CREATE DATABASE QUERY:
CREATE DATABASE DemoDatabase;
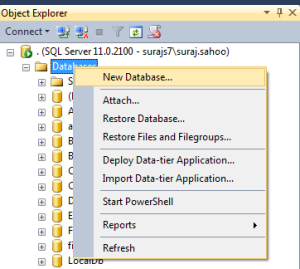
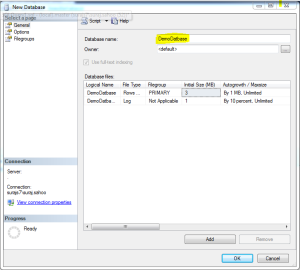
The above query using the master creates the database named “DemoDatabase”.You can also directly create database using the SSMS UI. See the below images.
When in the first image as you see, the New Database is clicked, another window pops upas shown in the second image. Add the database name and there and it creates the database for you with a maxsize of unlimited.
Then we create a Table for the storage of records.
CREATING A TABLE:
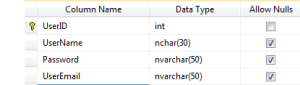
USE DemoDatabase CREATE TABLE [dbo].[User]( [UserId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [UserName] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Password] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [UserEmail] [nvarchar](50) NULL, CONSTRAINT [PK_User] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ( [UserId] )WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY] ) ON [PRIMARY]
Now the above query creates a table for you, but we need to understand the commands used in the query as some seem understandable where as some are not.
PAD_INDEX:- Specifies the index padding. The default is OFF. More info.
STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE:- Creation & Recreation of index & auto update of the columns statistics. More info.
ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS:- Enhances performances by locking the entire table rather than locking individual row. By default SQL sets to ON More info.
ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS:- Set to TRUE/ON when there are chances of high concurrency in order to improve performance. By default SQL sets to ON More info.
Thus, we have created a database which now has a table named User. Now for your information, we can also create table using the SSMS UI as we have done for the database.
We open up the database tree structure and find Tables as a chile tree under it.
We right click on that and select New Table, we get a different UI in the query window now asking for the column names and the datatypes also to set the Nullable/NonNullable with a check box, then lets view the images:
Add the Primary key column and set it as Primary Key like below:
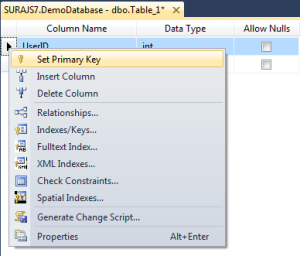 Then we need to set the column as an identity column which will be auto-incremented by 1 everytime a new row is added. The developer need not bother abput incrementing or setting the primary key. Set it as below:
Then we need to set the column as an identity column which will be auto-incremented by 1 everytime a new row is added. The developer need not bother abput incrementing or setting the primary key. Set it as below:
Then we add all the columns with the datatypes mentioned above and save the table with a proper table name. Now here the checkbox for the Nullable column plays a vital role. Think and specify the value here. Finally the UI looks like below:
Thus, now we have created a table also. Now it is time to add records/rows into it. We willbe writing queries to insert the values into the table. Lets see how:
INSERT ROWS INTO TABLE:
INSERT INTO dbo.[User] (UserName,Password,UserEmail)
VALUES ('Suraj','abc123','[email protected]');Here as you can see we have added only the three column values as the primary key userId is auto-incremented i.e. an Identity column. Thus, this adds the values. For a faster approach, usually developers use the SSMS UI here also to add the records.
We right click on the specific table into which we will be adding records, then click on Edit Top 200(default value) items.
Then we see in a new query window the table columns with the rows of records already added and a default empty row where we will be adding the values like below:
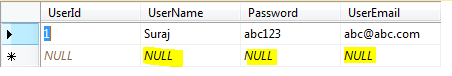 here we add the values in the row containing NULL values. The Primary key column is non editable as it will increment itself. The other columns are populated with the values to set the table records.
here we add the values in the row containing NULL values. The Primary key column is non editable as it will increment itself. The other columns are populated with the values to set the table records.
Now lets get back to our topic of discussion Select:
1. Select all records from the table:
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User]
This query is very simple and easy to understand. Here the FROM clause is used which is easy when we retrieve data from a single table. As mentioned above ‘*’ relates to all columns in a table. Thus, the above query returns all the records of all the columns.
Another, point here is if we select some columns out of all columns then we should/must qualify the column names in the Select list of the query.we can bring in the concept of ‘aliasing’ in our next query which selects some columns in the table.
2. Select fewer columns from the table:
SELECT users.UserName as Name, users.Password as PWD FROM dbo.[User] as users
The above query returns only the User name column as Name and the Password column as PWD in the result set. This is the power of alias, it changes the column head names. Below is the sample result set:
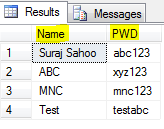 Similarly you can use shorter Table alias names and use it through out your query for convinence and select as many and the specific columns you need from the table.
Similarly you can use shorter Table alias names and use it through out your query for convinence and select as many and the specific columns you need from the table.
There are various ways for limiting the result sets we get. By default all the rows that match the From clause query are retrieved in the result set. There are two different ways to limit the result set of the Select statement.
One is to add conditions to the Query after From clause.
Anoother is to add the DISTINCT qualifier to the Select statement. Distinct is a result set qualifier. Also TOP (number) can be used to limit the result set.
We will see the second type here and move to the condition type consequently.
3. Select Distinct Rows :
SELECT DISTINCT users.UserName as Name FROM dbo.[User] as users;
This query returns all the rows that are distinct based on the names values.
4. Select some rows from TOP:
SELECT TOP 500 users.UserName as Name FROM dbo.[User] as users;
This would return only the top 500 rows no matter how many in total we get as result set.
Next we discuss about the conditions type:
WHERE Clause
This is used after the FROM clause and can be thought of a search from the records using the conditions based on which we would be doing the result search. Searching with lot more precision. The body of the where clause will be one or more expressions with return value as True/False. If the response is true based on the conditions for a specific row coming under the check, then the row gets added to the result set which is retrieved finally from the query.
A simple example here would be Get the list of records/users whose name is ‘Suraj’
5. Select users with UserName as ‘Suraj’:
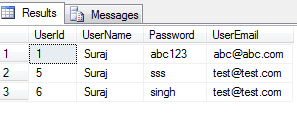
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName = 'Suraj' ;
This selects all the users with the username as Suraj, usually this is made as Firstname as Suraj. Thus the result set would look like below:
To master the WHERE clause in SQL we need to master how all the operators available behave. Lets have a look at the operators available with the WHERE clause in SQL and how would they behave:
| Datatype | Behaviour |
|---|---|
| Eqals ‘=’ | Returns true if both the conditions on left and right hand side matches |
| Not Equals to ‘<>’ | Returns true if both the conditions on left and right hand side do not match |
| Greater than ‘>’ | Returns true is the value on the left hand side is larger than the right hand side value |
| Less than ‘<‘ | Returns true is the value on the left hand side is smaller than the right hand side value |
| Greater than or equal to ‘>=’ | Returns true is the value on the left hand side is larger than or same as the right hand side value |
| Less than or equal to ‘<=’ | Returns true is the value on the left hand side is smaller than or same as the right hand side value |
Now lets have a look at the queries and how the behave when operators are applied. Here I will be applying operators on the string values.
6. Select the users with UserName greater than ‘Suraj’:
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName > 'Suraj' ;
The result set here would return the name starting with alphabets more than ‘S’, but remember the check is for each letter until the greater than matches. Result set:
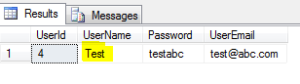 Thus the name starting with ‘T’is displayed in the result.
Thus the name starting with ‘T’is displayed in the result.
Similarly less than and the other operators would work out.
7. Select the users with UserName less than ‘Suraj’:
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName < 'Suraj' ;
8. Select the users with UserName not equal to ‘Suraj’ :
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName <> 'Suraj' ;
Then lets peep into the AND OR operators. As we all know each boolean expression can be combined with other boolean expressions. These are combined by using the AND OR operator.
AND means that both the boolean expressions combined by using AND, both must evaluate to True for the row to satisfy to be a part of the result set. Like for example list out the users who have first name as Suraj and email as a specific value. Here as per the simple english language and is to be used here to evaluate and produce the result set.
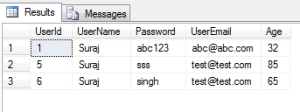
9. Select the users with UserName as ‘Suraj’ & UserEmail as ‘[email protected]’:
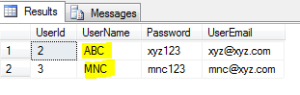
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName ='Suraj' AND users.UserEmail = '[email protected]';
The result set goes as below:
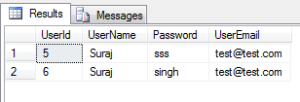 Thus here in the result set, we can check that both the expressions on the sides of the AND operator turm out to be true for both the rows in the result set.
Thus here in the result set, we can check that both the expressions on the sides of the AND operator turm out to be true for both the rows in the result set.
OR keyword means that any of the expressions on the either side of OR operator can be true, then the row becomes a part of the result set. That is when any of the expression satisfies then the row is a part. Just keep in mind if the first expression turns out to be true then the second expression is not evaluated. If first expression turns to be false, then the second expression is evaluated to be checked.
10. Select the users with UserName as ‘Suraj’ or UserEmail as ‘[email protected]’:
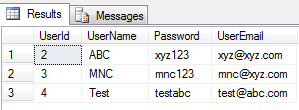
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName ='Suraj' OR users.UserEmail = '[email protected]';
The result set is as below:
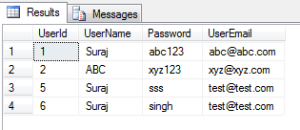 As we see first when the first expression i.e. UserName is Suraj is a part of the result set and also the rows with UserEmail as ‘[email protected]’ .
As we see first when the first expression i.e. UserName is Suraj is a part of the result set and also the rows with UserEmail as ‘[email protected]’ .
BETWEEN operator acts on any column and taking two values checking the range. If a row value lies in the range specified in the BETWEEN condition, then the expression evaluates to True.
11. Select the users with age lying between specific value:
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.Age BETWEEN 25 AND 50 ;
The result set is as below:
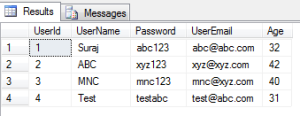 Thus the result set include only those rows where the Age lies between 25 and 50, others are neglected. Between in inclusive of the values being checked.
Thus the result set include only those rows where the Age lies between 25 and 50, others are neglected. Between in inclusive of the values being checked.
LIKE operator is a special one which is used with strings. When we give LIKE operator to the strings then it looks and search for those values of the string which match the pattern specified in the LIKE condition. For LIKE ‘%’ is used which is otherwise called wild card symbol. The % can be used anywhere in the string. Like for example, who all are the users whose names start with ‘S’.
12. Select the users with the UserName starting with letter ‘S’:
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName LIKE 'S%' ;
This gives the result with all the username starting with S. Thus we write Like ‘S%’ wild card symbol specified after the letter means starting with. Specifying wild card symbol at the beginning like ‘%S’ means all usernames ending with S.
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users WHERE users.UserName LIKE '%C' ;
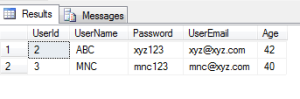 Thus this is the result set with the records where the column value UserName contains ‘C’.
Thus this is the result set with the records where the column value UserName contains ‘C’.
IN operator is another special operator which requires column and a list of specified/valued values. Values can be of any datatype. If a row column value matches any of the specified values in the list used for the IN operator, then the row is added to the result set.
SELECT * FROM dbo.[User] as users
WHERE users.UserName IN ('Suraj' , 'test') ;This gives the result set having all Users with user name Suraj and test. Thus the IN operator seems to overlap with the BETWEEN operator, but they are different in some scenarios.
IS operator is less used and a special keyword, which is usedto check for NULL values. An interesting thing to keep in mind is that the NULL values are not assignable to the ‘=’ operator & its complement is ISNOT.
Conclusion
Thus here I have tried to specify the basics in SQL. As I have mentioned I have tried here, so if any queries, suggestions & concerns are most welcome. Please raise lets discuss and clear out and keep sharing.
References
MSDN
Introduction to SQL by John Flanders.
SQL authority by Pinal Dave
W3 schools